10 Fun Facts About Pluto's Journey From Planet to Beloved Dwarf Planet
Pluto, once the ninth planet of our solar system, has undergone a remarkable cosmic transformation that has captivated astronomers and the public alike. Discovered in 1930 by American astronomer Clyde Tombaugh, Pluto was initially celebrated as the newest addition to our planetary family. Its distant orbit and icy composition made it a unique member of the solar system, sparking curiosity and wonder. However, as astronomical technology and understanding evolved, so too did our perception of Pluto. In 2006, the International Astronomical Union (IAU) reclassified Pluto as a "dwarf planet," a decision that stirred debate and emotion across the globe. This reclassification did not diminish Pluto's allure; instead, it enhanced its mystique, as scientists and enthusiasts alike sought to understand its true nature and significance. This article delves into Pluto's cosmic transformation, exploring 10 fascinating facts about its journey from a major planet to a beloved dwarf planet.
1. The Discovery of Pluto: A New Frontier

The discovery of Pluto marked a significant milestone in the field of astronomy. In the early 20th century, astronomers were on the hunt for a ninth planet, spurred by irregularities in the orbits of Uranus and Neptune that suggested the presence of another gravitational force. Clyde Tombaugh, a young astronomer working at the Lowell Observatory in Flagstaff, Arizona, took on the challenge. Using a technique called "blink comparison," Tombaugh meticulously compared photographic plates of the night sky, searching for any movement that would indicate a new celestial body. After months of painstaking work, he finally spotted a faint object moving against the backdrop of stars. This object, later named Pluto, was hailed as the ninth planet of our solar system. Pluto's discovery was a triumph of persistence and ingenuity. It was also a testament to the power of human curiosity and the desire to explore the unknown. The excitement surrounding Pluto's discovery was palpable, as it represented a new frontier in our understanding of the solar system. It was a moment that captured the imagination of the public and inspired a generation of astronomers to continue the search for new worlds. However, as we would later learn, Pluto's story was far from complete, and its discovery was just the beginning of a much larger cosmic journey.
2. : A Major Planet

Upon its discovery, Pluto was classified as the ninth planet of the solar system, a status it held for over seven decades. This classification was based on the limited knowledge and technology available at the time. Pluto's size and distance from the sun suggested it was similar to the other planets, albeit with some unique characteristics. Its icy composition and eccentric orbit set it apart, but these features were not fully understood until much later. During this period, Pluto was embraced as a major planet, and its inclusion in the planetary lineup was celebrated by both scientists and the public. Pluto's initial classification as a major planet was a reflection of the astronomical knowledge of the early 20th century. At the time, the criteria for defining a planet were not as rigorous or well-defined as they are today. The discovery of Pluto was a significant achievement, and its classification as a planet was a natural extension of the excitement and curiosity it inspired. However, as our understanding of the solar system evolved, so too did the criteria for what constitutes a planet. This would eventually lead to Pluto's reclassification and a broader redefinition of what it means to be a planet.
3. The Rise of Planetary Science: A New Perspective

The mid-20th century saw significant advancements in planetary science, driven by new technologies and a growing interest in the exploration of our solar system. The development of more powerful telescopes, space probes, and computer simulations allowed scientists to study celestial bodies in unprecedented detail. These advancements led to a deeper understanding of the solar system's formation and the processes that govern planetary dynamics. As a result, astronomers began to question the traditional definitions of planets and sought a more precise classification system. This period of scientific progress brought new perspectives on Pluto and its place in the solar system. Researchers discovered that Pluto's orbit was highly eccentric and inclined, unlike the orbits of the other planets. Additionally, its size was found to be much smaller than initially thought, comparable to that of some of the largest moons in the solar system. These findings prompted scientists to reconsider Pluto's status as a planet and explore alternative classifications. The rise of planetary science set the stage for a more nuanced understanding of celestial bodies and ultimately led to the redefinition of what it means to be a planet.
4. The Kuiper Belt: Pluto's True Neighborhood

One of the most significant discoveries in planetary science was the identification of the Kuiper Belt, a region of the solar system beyond Neptune populated by icy bodies and dwarf planets. The existence of the Kuiper Belt was first proposed by astronomer Gerard Kuiper in 1951, but it was not until the 1990s that direct evidence of its existence was obtained. The discovery of numerous small, icy objects in this region, collectively known as Kuiper Belt Objects (KBOs), provided new context for understanding Pluto's place in the solar system. The Kuiper Belt challenged the traditional view of the solar system as a collection of planets orbiting in a flat, orderly plane. Instead, it revealed a more complex and dynamic environment, with a diverse array of celestial bodies. Pluto, with its icy composition and eccentric orbit, was found to be more similar to KBOs than to the traditional planets. This realization prompted astronomers to reconsider Pluto's classification and explore its relationship with other objects in the Kuiper Belt. The discovery of the Kuiper Belt was a pivotal moment in Pluto's cosmic transformation, providing a framework for understanding its unique characteristics and redefining its status within the solar system.
5. The 2006 IAU Decision: Redefining Planethood

In 2006, the International Astronomical Union (IAU) convened to address the growing need for a clear and precise definition of what constitutes a planet. This meeting was prompted by the discovery of several large KBOs, including Eris, which was similar in size to Pluto. The IAU recognized that the traditional definition of a planet was no longer sufficient to encompass the diversity of celestial bodies in the solar system. After much debate, the IAU established three criteria for defining a planet: it must orbit the sun, be spherical in shape due to its own gravity, and have cleared its orbital path of other debris. Pluto met the first two criteria but failed to meet the third, as its orbit overlaps with other objects in the Kuiper Belt. As a result, Pluto was reclassified as a "dwarf planet," a decision that sparked controversy and debate among scientists and the public. The IAU's decision was a reflection of the evolving nature of science and the need to adapt our understanding as new information becomes available. While the reclassification was initially met with resistance, it ultimately provided a more accurate framework for understanding the diverse array of celestial bodies in our solar system.
6. The Public Reaction: A Planetary Identity Crisis

The reclassification of Pluto as a dwarf planet in 2006 was met with a strong public reaction, as many people felt a deep emotional connection to Pluto as the ninth planet. For decades, Pluto had been a beloved member of the solar system, featured in textbooks, planetariums, and popular culture. Its demotion to dwarf planet status was seen by some as a loss, sparking protests, petitions, and even campaigns to "Save Pluto." This reaction highlighted the powerful role that celestial bodies play in our collective imagination and the emotional ties we form with them. The public's response to Pluto's reclassification also underscored the intersection of science and culture. While the IAU's decision was based on scientific criteria, it had a profound impact on how people perceived the solar system and their place within it. The debate over Pluto's status became a cultural phenomenon, with discussions taking place in classrooms, online forums, and media outlets around the world. This planetary identity crisis prompted many to reflect on the nature of scientific progress and the ways in which our understanding of the universe continues to evolve.
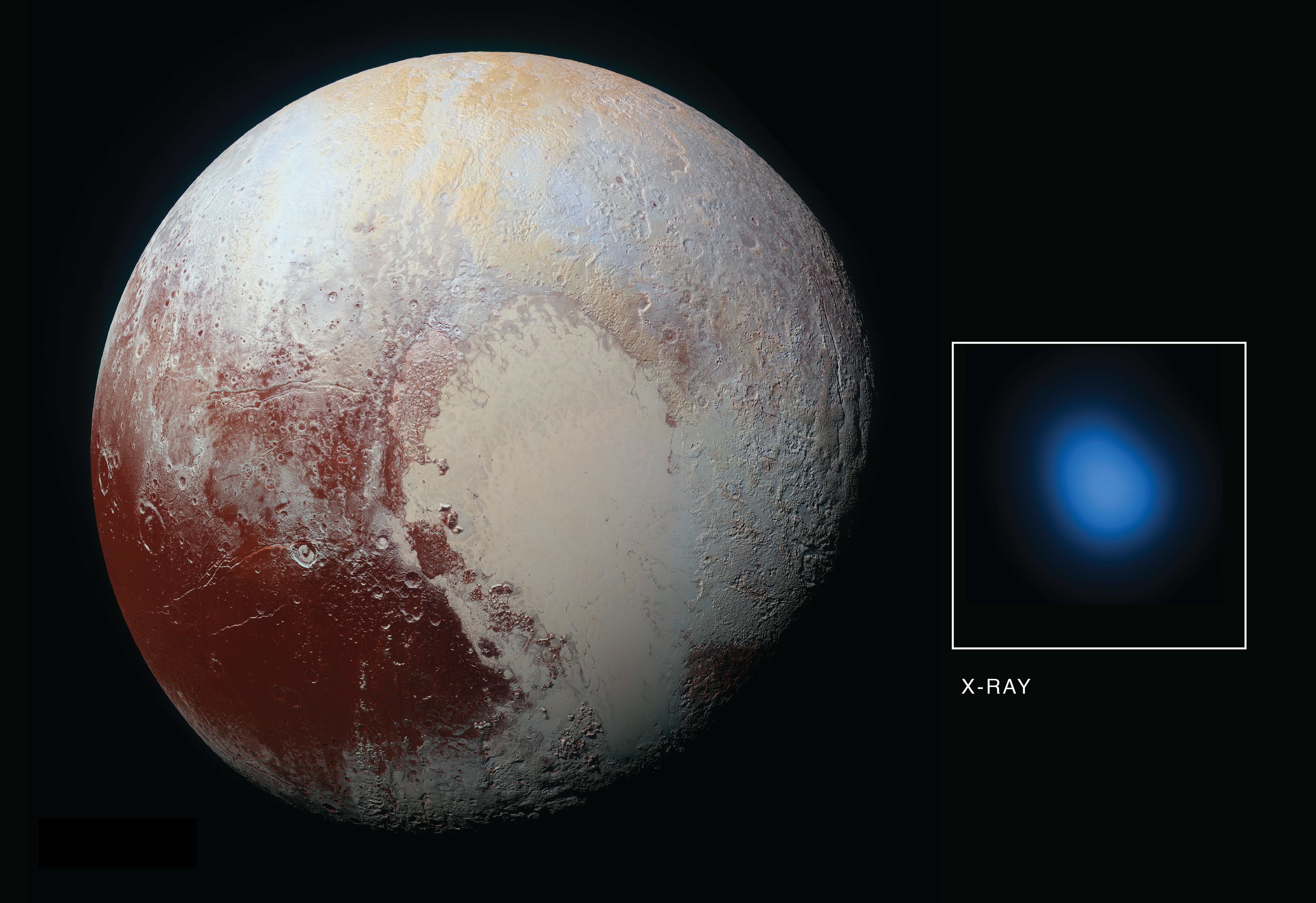
7. New Horizons: Unveiling Pluto's Mysteries
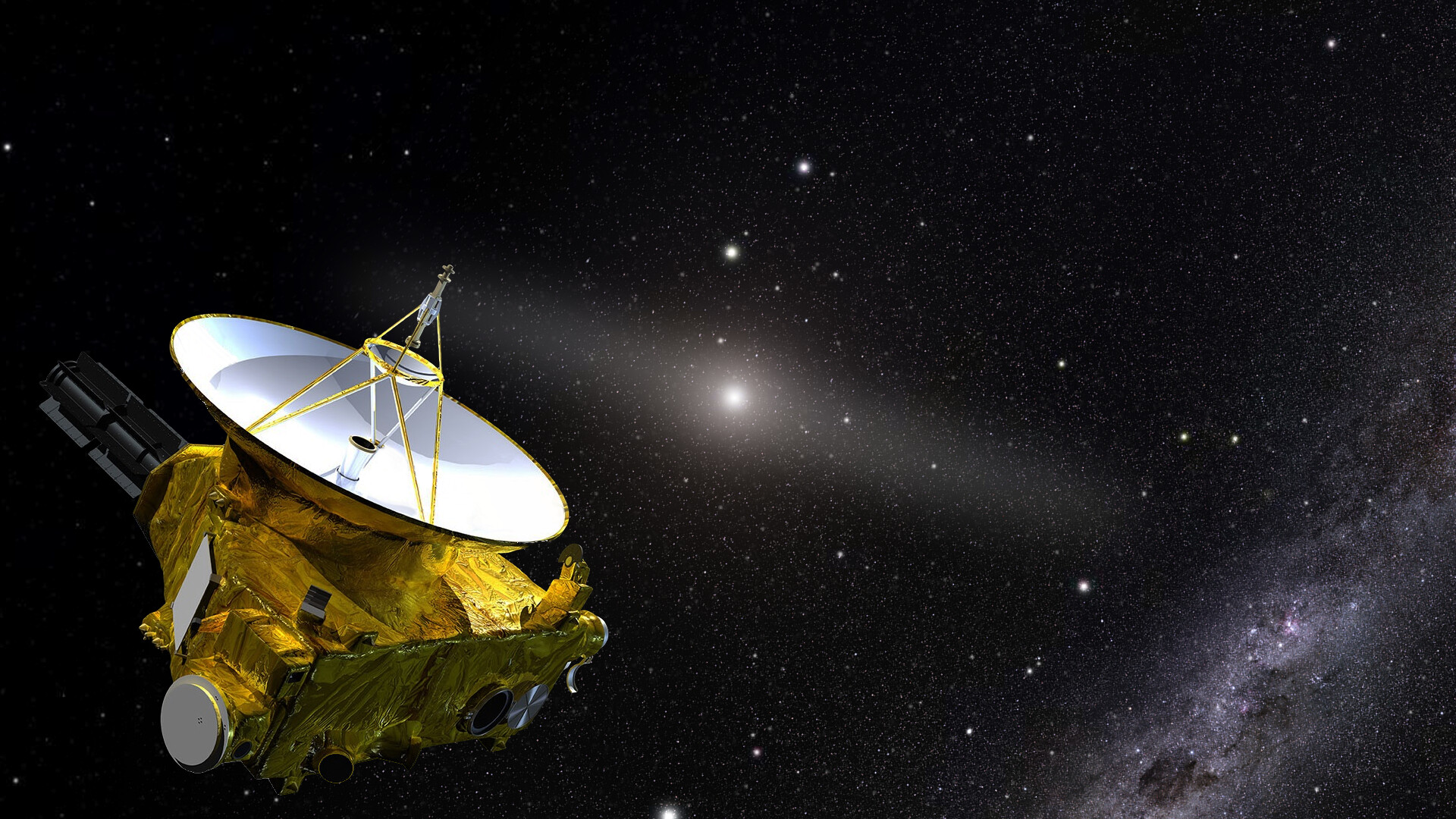

In 2015, NASA's New Horizons spacecraft made history by conducting the first-ever flyby of Pluto, providing an unprecedented glimpse into the distant dwarf planet. Launched in 2006, New Horizons traveled over nine years and three billion miles to reach Pluto, capturing stunning images and data that transformed our understanding of this enigmatic world. The mission revealed a landscape of surprising complexity, with towering mountains of water ice, vast plains of frozen nitrogen, and a thin atmosphere composed of nitrogen, methane, and carbon monoxide. The New Horizons mission was a triumph of human ingenuity and a testament to the enduring fascination with Pluto. The data collected by the spacecraft provided new insights into Pluto's geology, atmosphere, and potential for hosting organic compounds. It also sparked renewed interest in the Kuiper Belt and the broader study of icy worlds in the outer solar system. The success of New Horizons demonstrated the power of exploration and the potential for future missions to uncover even more mysteries about Pluto and its cosmic neighborhood.
8. Pluto's Moons: A Complex System
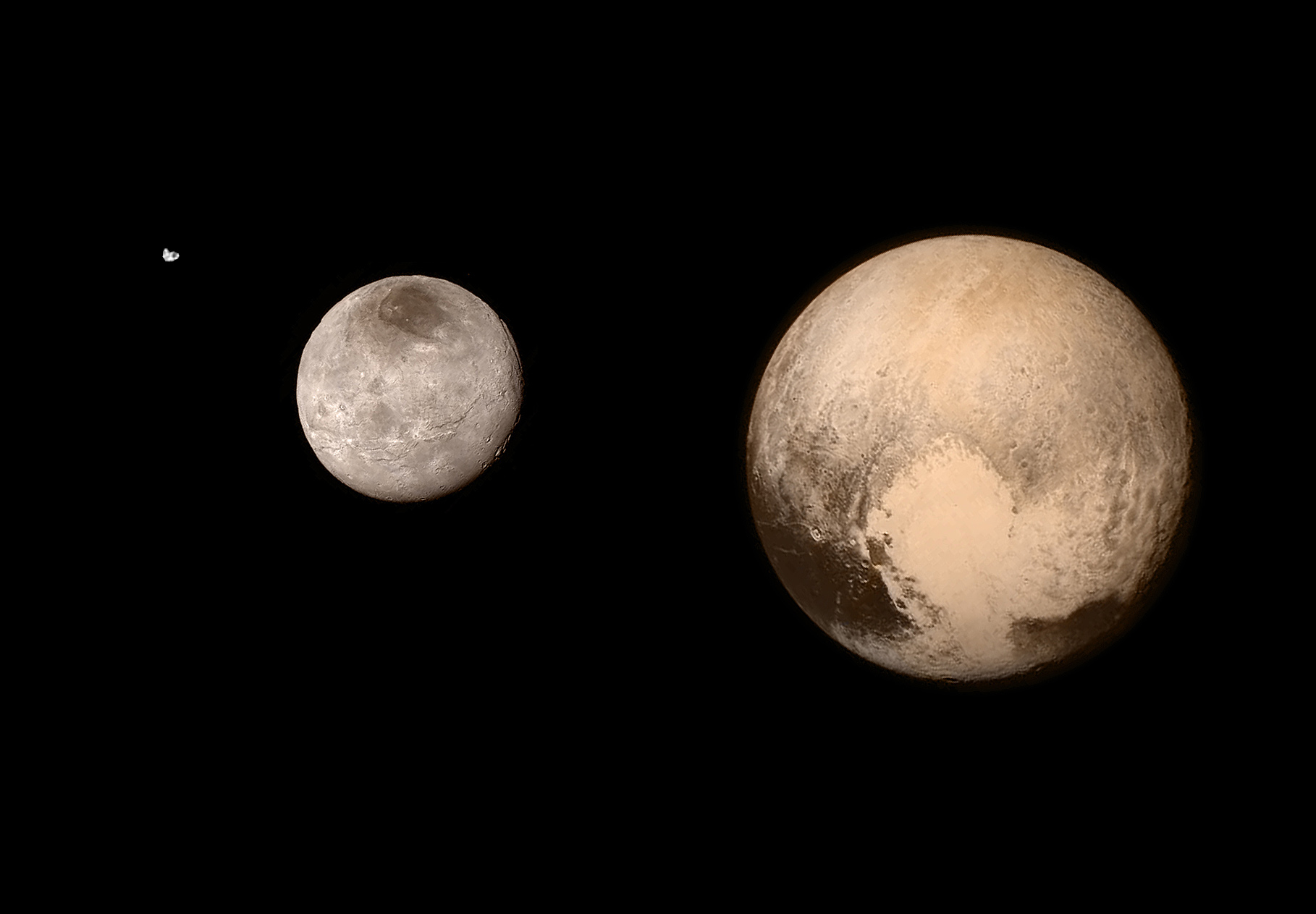

Pluto is not alone in its journey through the Kuiper Belt; it is accompanied by a system of five known moons, each with its own unique characteristics. The largest of these moons, Charon, is nearly half the size of Pluto and is gravitationally locked in a mutual orbit with the dwarf planet. This close relationship has led some astronomers to consider Pluto and Charon a binary system, as they orbit a common center of mass located outside of Pluto itself. In addition to Charon, Pluto is orbited by four smaller moons: Styx, Nix, Kerberos, and Hydra. These moons were discovered in the 21st century, thanks to advances in telescopic technology and the efforts of astronomers dedicated to exploring the outer solar system. The dynamics of Pluto's moons provide valuable insights into the processes that govern the formation and evolution of celestial bodies in the Kuiper Belt. The study of these moons continues to shed light on the complex interactions between Pluto and its cosmic companions.
9. Cultural Impact: Pluto in Popular Imagination

Pluto's journey from major planet to adored dwarf planet has had a significant impact on popular culture, inspiring a wide range of artistic expressions and media representations. From literature and film to music and art, Pluto has captured the imagination of creators and audiences alike. Its enigmatic nature and distant location have made it a symbol of mystery and exploration, often serving as a backdrop for stories of adventure and discovery. The cultural impact of Pluto extends beyond entertainment, influencing educational initiatives and public engagement with science. The debate over Pluto's status has sparked interest in astronomy and encouraged people of all ages to learn more about the solar system. Pluto's story has become a powerful tool for science communication, illustrating the dynamic nature of scientific inquiry and the ways in which our understanding of the universe continues to evolve. As a beloved member of the cosmic family, Pluto's influence on popular imagination remains strong, inspiring future generations to explore the mysteries of the cosmos.
10. Scientific Legacy: Pluto's Role in Astronomy
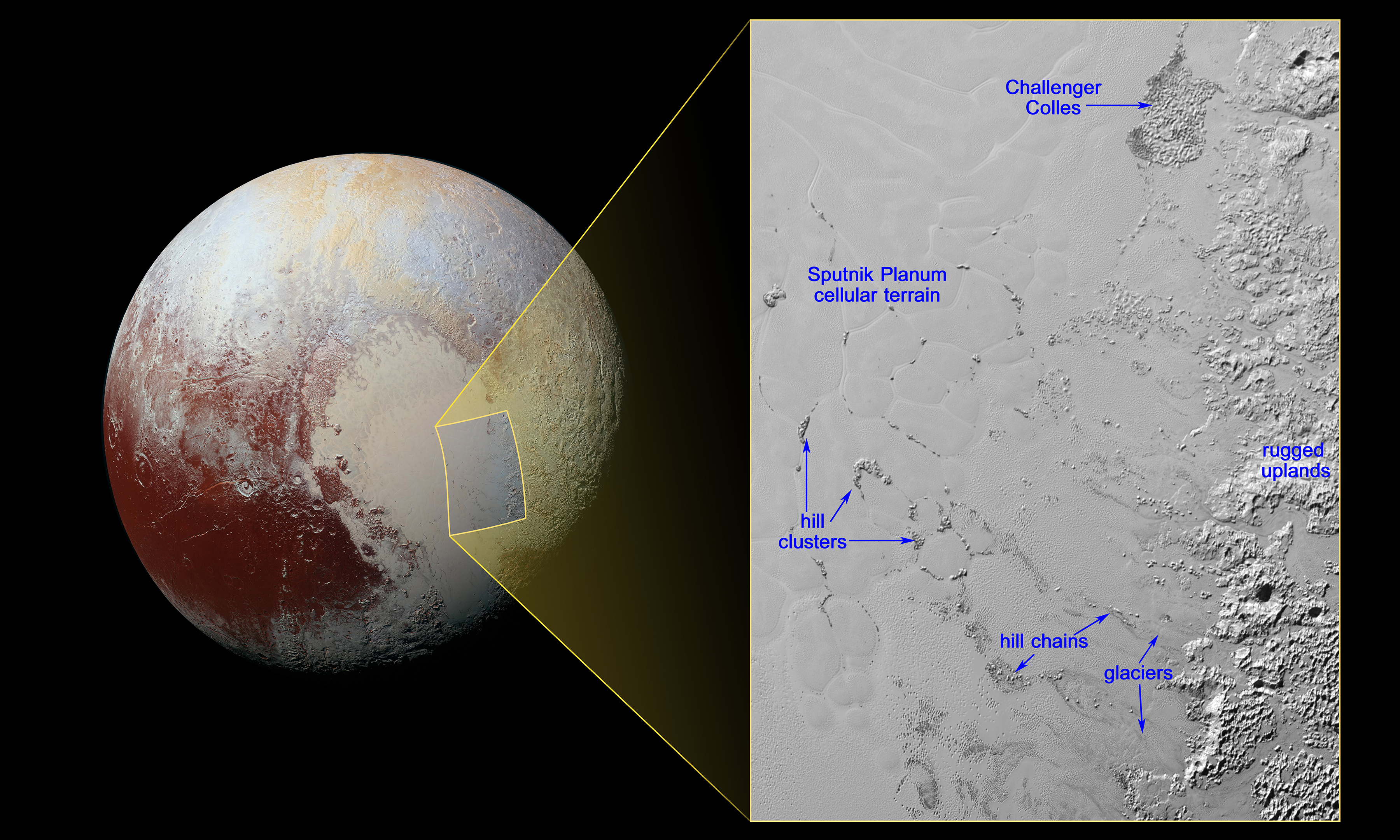
Pluto's reclassification as a dwarf planet has had a lasting impact on the field of astronomy, prompting a reevaluation of planetary definitions and the study of celestial bodies. The debate over Pluto's status has led to a more nuanced understanding of the solar system and the criteria used to classify planets. This has opened the door to new research opportunities and a deeper exploration of the outer solar system, including the study of Kuiper Belt Objects and other distant worlds. Pluto's scientific legacy is also reflected in the advancements in technology and methodology that have emerged as a result of its study. The development of new telescopes, spacecraft, and analytical techniques has enabled astronomers to gather more detailed data and make more accurate observations. These advancements have not only enhanced our understanding of Pluto but have also contributed to the broader study of planetary science and the search for life beyond Earth. As a catalyst for scientific progress, Pluto continues to play a vital role in shaping the future of astronomy.
Pluto's cosmic transformation from a major planet to an adored dwarf planet is a testament to the dynamic nature of science and the ever-evolving understanding of our universe. Its journey has captivated the imagination of scientists and the public alike, inspiring curiosity and exploration. From its discovery in 1930 to the groundbreaking New Horizons mission, Pluto has remained a symbol of the mysteries that lie beyond our reach, inviting us to explore and discover. Pluto's enduring legacy is one of scientific progress and cultural impact. It has challenged our perceptions, expanded our knowledge, and inspired a deeper appreciation for the complexity of the cosmos. As we continue to explore the outer reaches of the solar system, Pluto serves as a reminder of the boundless possibilities that await us in the quest for understanding. Its story is a celebration of the human spirit of exploration and the relentless pursuit of knowledge, ensuring that Pluto will remain a cherished member of our cosmic family for generations to come.







