11 Weird Laws About Random Objects Around The World
In the vast tapestry of global legal systems, some threads stand out due to their sheer peculiarity. These are the laws that govern objects in ways that might seem bizarre, even whimsical, to the uninitiated. These object laws, scattered across continents and cultures, reveal much about the societies that birthed them. They speak to historical quirks, cultural values, and sometimes, sheer happenstance. This article embarks on a journey through 11 such laws, each a testament to human creativity and the diverse ways in which societies attempt to regulate the tangible world. As we delve into these laws, we will uncover not just the statutes themselves, but the stories and rationales that underpin them, offering a window into the rich tapestry of human civilization.
1. The Swiss Toilet Flush Ban

Switzerland, renowned for its precision and order, holds a law that surprises many: the prohibition of flushing toilets after 10 PM in apartment buildings. This regulation is rooted in the country's commitment to noise pollution control, reflecting the Swiss dedication to community harmony and respect for personal space. While it may seem extreme, this law underscores a societal emphasis on tranquility and the protection of peaceful living environments. The law's existence raises questions about balancing individual freedom with communal well-being, a theme that resonates in many legal systems worldwide.
2. The UK's Ban on Handling Salmon Suspiciously

In the United Kingdom, handling salmon with suspicion is an offense under the Salmon Act of 1986. This peculiar law was introduced to curb illegal salmon poaching, a serious issue impacting both the economy and the environment. The law illustrates how specific legal language can sometimes lead to humorous interpretations. While it targets a genuine problem, its phrasing has become a source of amusement and curiosity, highlighting the challenges lawmakers face in crafting legislation that is both effective and clear.
3. The French Law on Flying Saucer Landings

In Châteauneuf-du-Pape, a small French town famed for its wine, a local ordinance prohibits the landing of flying saucers. Enacted in 1954 during a period of heightened UFO sightings, this law reflects the cultural zeitgeist of the time. While the regulation is more symbolic than practical, it serves as a reminder of the ways in which societal fears and fascinations can manifest in legal codes. This law also illustrates the interplay between local governance and global phenomena, as communities grapple with issues that transcend borders.
4. The Canadian Coinage Act Limitation

Canada's Currency Act restricts the number of coins that can be used in a single transaction. This law, limiting transactions to a maximum of 25 pennies, was designed to prevent nuisance payments and ensure smoother commercial exchanges. It highlights the practical challenges of currency management and the need for regulations that facilitate economic efficiency. This law also prompts reflection on the evolution of money and the ways in which legal systems adapt to changing economic landscapes, such as the rise of digital transactions.
5. The Singaporean Chewing Gum Ban

Singapore's ban on chewing gum is one of the most famous object laws, introduced to maintain public cleanliness and infrastructure integrity. The ban, implemented in 1992, aimed to curb the costly and time-consuming task of cleaning gum litter from public spaces. This regulation underscores Singapore's broader approach to governance, characterized by strict laws and high standards of public order. It also raises questions about the balance between individual freedoms and societal benefit, a recurring theme in discussions about governance.
6. The Italian Goldfish Bowl Ban
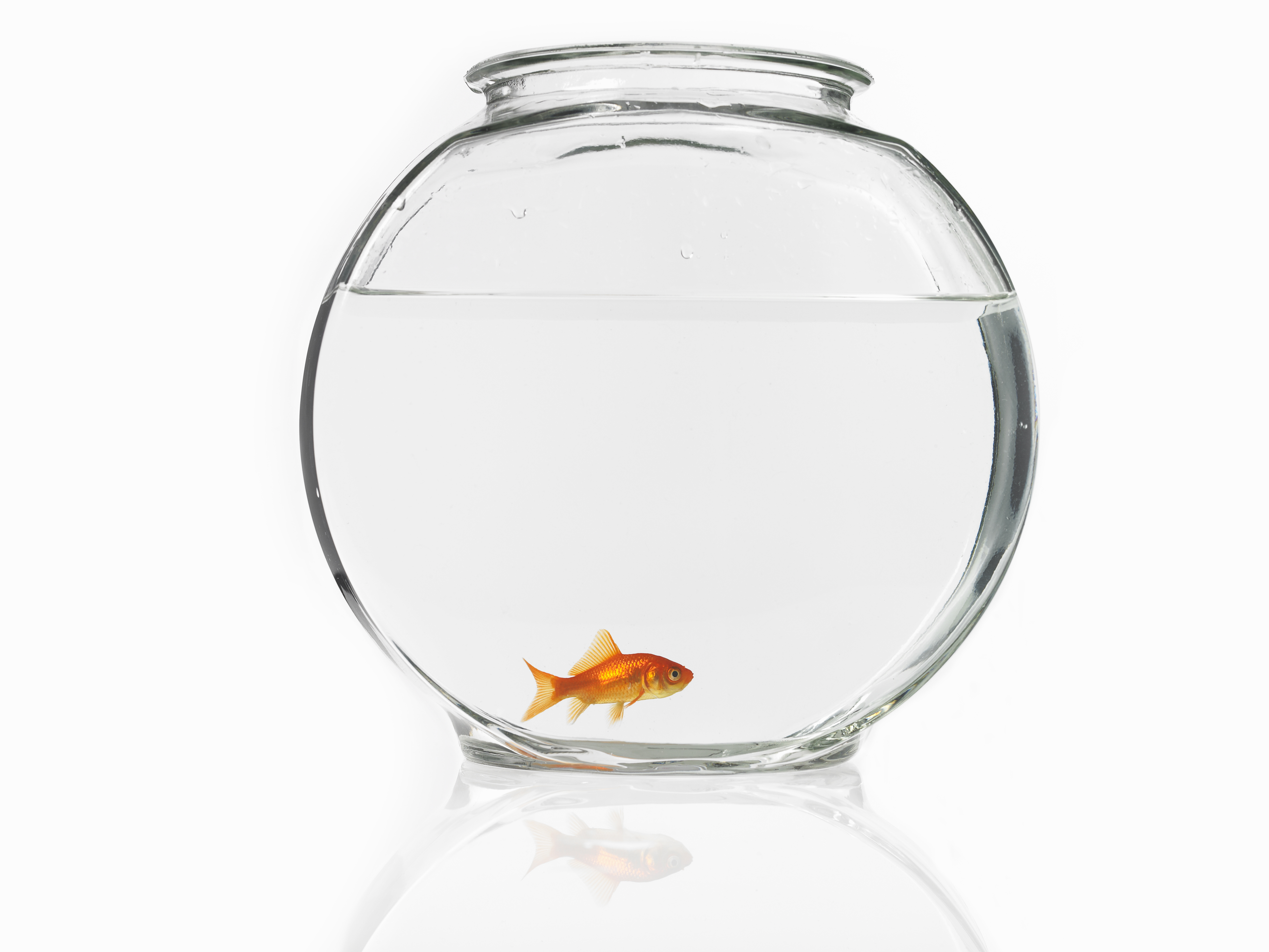

In Rome, Italy, a law prohibits the use of spherical goldfish bowls. This regulation was enacted to prevent animal cruelty, as the bowls are believed to cause fish to suffer disorientation and poor oxygenation. This law reflects a broader societal commitment to animal welfare and the ethical considerations that underpin it. It also highlights the ways in which cultural attitudes towards animals can shape legal frameworks, prompting broader discussions about the rights and treatment of non-human entities.
7. The Japanese Law on Dancing After Midnight

For many years, Japan had a law prohibiting dancing after midnight in public venues. Enacted in 1948, this law was originally intended to curb prostitution and maintain public morals. While largely unenforced in modern times, the law remained on the books until its repeal in 2015. This regulation illustrates the ways in which historical contexts can shape legal landscapes long after the original conditions have changed. It also highlights the tension between tradition and modernity in rapidly evolving societies.
8. The Thai Ban on Stepping on Currency

In Thailand, stepping on currency is illegal, as it is considered an act of disrespect towards the monarchy. Thai banknotes and coins bear the image of the king, and thus, are treated with great reverence. This law underscores the deep cultural respect for the monarchy and the ways in which this reverence is codified into law. It also highlights the intersection of cultural values and legal systems, prompting reflection on how societal norms are enforced through legislation.
9. The American Law Against Carrying Ice Cream Cones in Pockets

In parts of the United States, it is illegal to carry an ice cream cone in your pocket. This law, originating from the late 19th century, was intended to prevent horse theft, as thieves would use cones to lure horses away. While the law may seem absurd today, it reflects historical contexts and the innovative (if misguided) methods people employed. This regulation serves as a reminder of the dynamic nature of legal systems and the ways in which they evolve in response to changing societal needs.
10. The Australian Law on Changing Light Bulbs

In Victoria, Australia, changing a light bulb without a licensed electrician was once illegal. This regulation was part of broader electrical safety laws aimed at reducing accidents and ensuring proper standards. While the law has since been relaxed, it highlights the ways in which safety concerns can lead to highly specific legal requirements. This law also raises questions about the balance between safety and personal responsibility, a theme that resonates in many areas of public policy.
11. The Russian Law on Dirty Cars
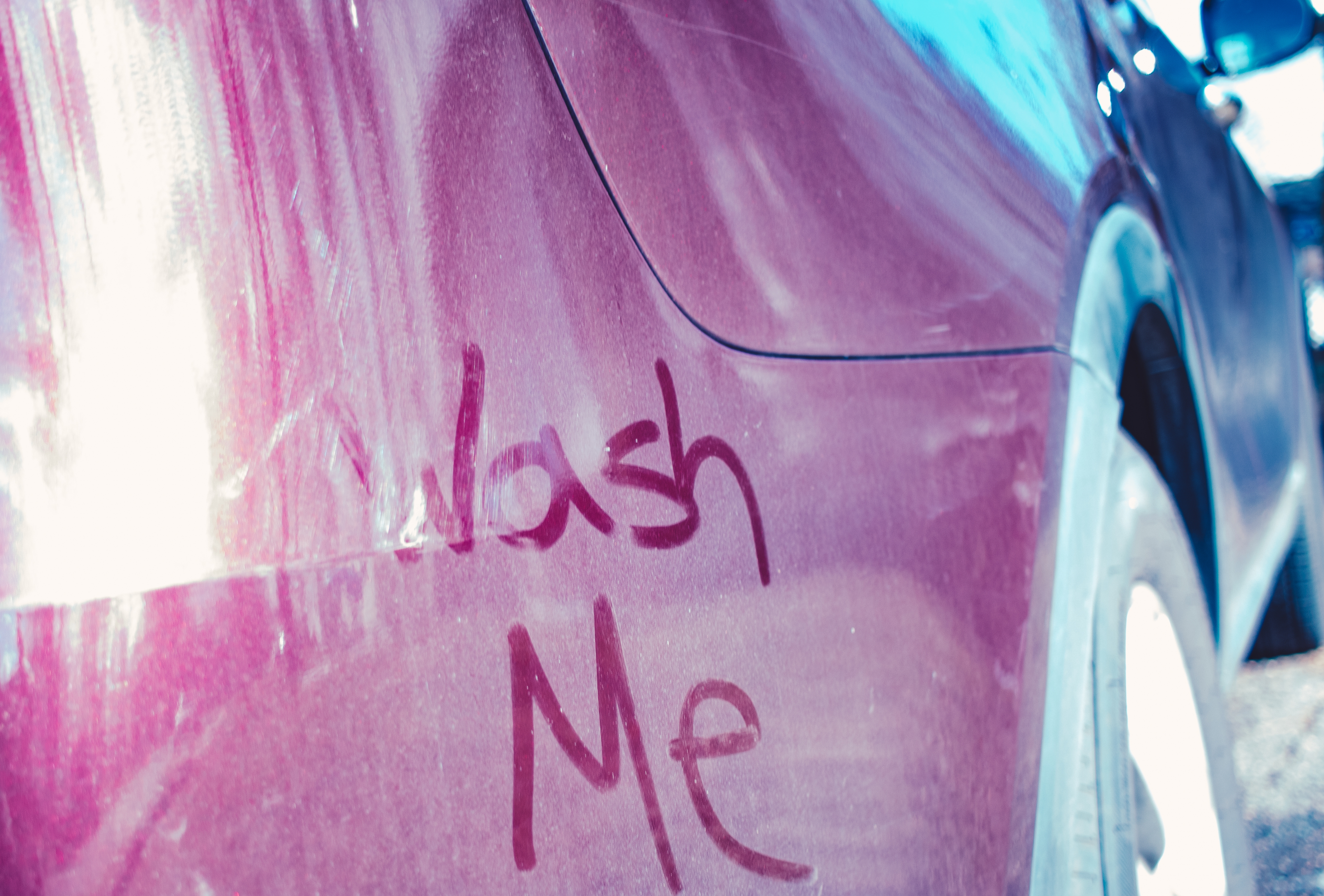
In Russia, driving a dirty car can result in a fine, particularly in Moscow. This law, aimed at maintaining urban cleanliness and improving the city's image, reflects broader societal values around order and aesthetics. It also underscores the practical challenges cities face in managing public spaces and the ways in which legal systems attempt to address these challenges. This regulation prompts reflection on the role of law in shaping public behavior and the ways in which legal codes reflect cultural priorities.
The Tapestry of Object Laws

These 11 object laws, each unique in its origin and intent, offer a fascinating glimpse into the diverse ways societies regulate the material world. They reveal much about cultural values, historical contexts, and the complexities of governance. As we journey through these laws, we gain insight into the human condition and the myriad ways in which societies strive to balance order, freedom, and justice. These laws, while sometimes humorous or peculiar, are a testament to the creativity and adaptability of human legal systems, reflecting the ever-evolving tapestry of human civilization.







